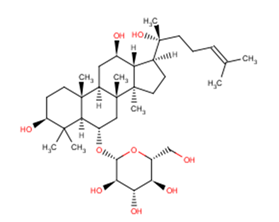
(20R)-Ginsenoside Rh1
CAS No. 80952-71-2
(20R)-Ginsenoside Rh1( —— )
Catalog No. M19132 CAS No. 80952-71-2
20S, 20R ginsenoside-Rh1 can inhibit the thrombin-induced conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 157 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(20R)-Ginsenoside Rh1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description20S, 20R ginsenoside-Rh1 can inhibit the thrombin-induced conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
-
Description20S, 20R ginsenoside-Rh1 can inhibit the thrombin-induced conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number80952-71-2
-
Formula Weight638.9
-
Molecular FormulaC36H62O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (156.53 mM)
-
SMILESO1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1CO)O)O)O)O[C@@H]1[C@H]2C([C@H](CC[C@@]2([C@@H]2[C@@](C1)([C@@]1(CC[C@@H]([C@H]1[C@@H](C2)O)[C@@](C)(CCC=C(C)C)O)C)C)C)O)(C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Yu HS,et al. [Chemical constituents from processed rhizomes of Panax notoginseng]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;38(22):3910-7.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-Acetamidophenol
2-Acetamidophenol (Orthocetamol) has analgesic and antipyretic effects. 2-Acetamidophenol is an isomer of Paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol).
-
CB-839
CB-839 (Telaglenastat) is a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of glutaminase with IC50 of 28 and 23 nM for glutaminase in kidney and brain (GAC and KGA).
-
5-O-Cinnamoylquinic ...
5-O-Cinnamoylquinic acid is a nature product.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


